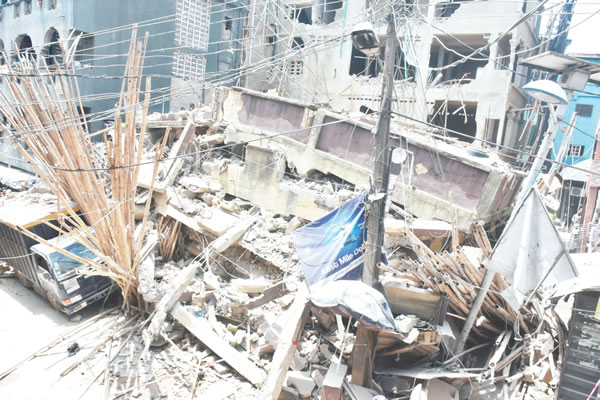
The loss of 22 lives in the collapsed two-storey building in Jos, Plateau State has thrown up once again, the overriding need to adhere to building insurance codes, writes JOSEPH INOKOTONG.
The collapse of a two-storey building at Saint Academy in the city of Jos, Plateau State capital last week has once again brought to the fore the issue of building insurance.

In that incident, at least 22 people died in the collapse, and 132 others were hospitalised, with victims still being counted on Friday night, according to local officials. The number found dead or injured in the rubble of the private school was still climbing and dozens, including many students, remained trapped, authorities said.
Building insurance, also known as property insurance or hazard insurance, is a type of insurance policy that provides financial protection against losses or damage to a building or structure caused by a variety of perils, including fire, wind, hail, lightning, and vandalism.
Building insurance can be purchased by homeowners, renters, and business owners to protect their properties from damage or destruction. It typically covers the cost of repairs or replacement of the building, as well as any personal property inside the building that may be damaged or destroyed.
Among the top compulsory insurance policies in Nigeria for individuals and businesses, which the National Insurance Commission (NAICOM) has been spearheading enforcement is the Insurance of Buildings Under Construction in Nigeria.
The Insurance of Buildings Under Construction policy is an essential requirement for anyone involved in the construction or ownership of multi-storey buildings in Nigeria. It provides a safety net against potential risks that may arise during the construction process.
This policy stipulates that contractors, owners, and agents are held accountable for any negligence that may result in bodily harm, property damage, or fatality to the public. By complying with this policy, stakeholders can guarantee the safety of their projects and mitigate potential financial losses. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritise the Insurance of Buildings Under Construction policy to ensure the success of any construction project in Nigeria.
Failure to obtain Insurance for Buildings Under Construction in Nigeria can result in severe penalties, including a fine of N250,000, three years imprisonment, or both.
In the case of Jos building, it is not certain if the owner followed laid down rules during and before the construction.
Insurance plays a vital role in mitigating building collapse in terms of risk transfer. It can provide financial protection for property owners, transferring the risk of loss from the property owner to the insurance company. In risk prevention, Insurance companies can use incentives and requirements to encourage property owners to take steps to prevent building collapse, such as regular inspection and maintenance.
Risk remediation entails an Insurance firm providing funds for rebuilding and recovery after a collapse, helping property owners to get back on their feet.
Insurance coverage can vary depending on the type of policy and the insurance company. Some policies may exclude coverage for damage caused by natural disasters or acts of terrorism.
Insurance companies may require property owners to take steps to reduce the risk of collapse, such as performing regular structural inspections or installing seismic retrofits.
Insurance may also cover the cost of debris removal and environmental cleanup after a collapse, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
To minimise the risk of building collapse, owners must adhere to building codes and regulations as they are designed to ensure that buildings are safe and structurally sound.
Regular inspecting and maintaining a building can help to identify potential structural issues before they become a problem, and overloading a building with too much weight should be avoided because it can weaken the structure and increase the risk of collapse.
Insurance can assist in reducing the risk of building collapse by encouraging adherence to building codes and regulations. Insurance companies may require adherence to building codes and regulations as a condition of coverage. It can also provide incentives for regular inspection and maintenance by offering discounts or other incentives for customers who regularly inspect and maintain their buildings. Providing coverage for damage and loss is one of the ways insurance companies can help mitigate the risk of building collapse. This can be done by providing financial protection for property owners in the event of a collapse, which can help to encourage them to take steps to reduce the risk of collapse.
When a building collapses, the following risk mitigation steps can be taken: Evacuation. This ensures that everyone is safely evacuated from the building and the surrounding area.
Search and rescue is the process of conducting search and rescue operations to locate and rescue any people who may be trapped in the rubble.
Recovering the bodies of those who lost their lives in the collapse and identifying them is another step, while investigation means conducting an enquiry to determine the cause of the collapse and identify any contributing factors.
It is pertinent to note that in building insurance, there are coverage limits. Most building insurance policies have coverage limits that specify the maximum amount the insurance company will pay for a covered loss. A deductible is the amount of money paid out of pocket before an insurance company will start paying for your claim. Most property insurance policies have a deductible, and the higher the deductible, the lower the premium. So, there is a need to decide how much you are willing to pay out of pocket in the event of a claim.
Building insurance policies often exclude coverage for certain types of damage, such as damage caused by flooding or earthquakes, known as exclusions.
Building insurance policies can have different types of loss settlement provisions, including replacement cost coverage, which pays the full cost of rebuilding or repairing the property, and actual cash value coverage, which pays the depreciated value of the property.
Also, Building insurance policies may include coverage for additional expenses, such as the cost of living in a hotel while the property is being repaired, or the cost of debris removal after a collapse.
However, property insurance is a type of insurance that covers damage or loss to physical property, such as a home or car. There are different types of property insurance, but the most common types are homeowners insurance and auto insurance.
Homeowners insurance covers damage to the home and its contents, while auto insurance covers damage to car. Property insurance is usually optional, but it is important to have if one owns valuable property that needs protection.
Experts are quick to add that property insurance provides protection against most risks to property, such as fire, theft, and some weather damage. This includes specialised forms of insurance such as fire insurance, flood insurance, earthquake insurance, home insurance, or boiler insurance.
Owning or renting a property can come with unpleasant surprises because the house could get damaged by a fire, an apartment could get damaged by a burst pipe or someone could break into the house and steal valuables. If guests accidentally injure themselves on a property and the owner is legally liable, they could sue for medical bills.
These scenarios could put a homeowner in a difficult financial situation, but having the right property insurance can serve as a protection against these potential pitfalls.
Property insurance covers many risks when one owns or rents a property. This coverage can include home insurance, renters insurance, landlord insurance or mobile home insurance. Property insurance may also provide supplemental coverage to help when standard home and renters insurance does not help, such as flood insurance and earthquake insurance.
Most property insurance policies include coverage for personal belongings and personal liability insurance. Each type of property insurance policy offers different coverage. For example, homeowners insurance includes dwelling coverage, while renters insurance does not pay for damage to a building or house. Landlord insurance instead covers the building and shared spaces, such as lobbies and staircases.
If there is a bodily injury or property damage claim against the homeowner, liability insurance pays for the legal fees and covers the other person’s losses. However, it is always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to protecting the property.
There are a few things to consider before getting property insurance. The need to determine how much coverage is needed stands out. One should also think about the type of property that needs to be insured, as well as any special risks or circumstances that might affect the coverage.
In this regard, there are a few things to keep in mind when choosing a property insurance policy. First, is the need to determine the value of the property to be insured. This is usually done by getting an appraisal from a qualified professional. Next, is to decide what type of policy you want. There are several different types of property insurance policies, including replacement cost policies, actual cash value policies, and guaranteed replacement cost policies.
A replacement cost policy will pay to replace a property with new property of similar kind and quality, regardless of depreciation. An actual cash value policy will pay to replace a property, but it will take depreciation into account. A guaranteed replacement cost policy will pay to replace a property, regardless of the cost. So, the main difference between these policies is how depreciation is handled.
Most property insurance policies cover the main dwelling, as well as other structures on the property, such as a garage, shed, or fence. The policy will also typically cover personal belongings, like furniture, clothes, and electronics. All policies are not the same, therefore, it is important to read the policy carefully to see what is covered.
Additional things that may be covered by a property insurance policy include living expenses if the homeowner is unable to live in the home while it is being repaired. This is called loss of use coverage. Some policies will also cover identity theft protection or credit monitoring services.
Liability coverage can help protect the homeowner if sued for an accident that occurs on the property.
Property insurance typically does not cover certain types of damage. For example, most policies won’t cover damage caused by earthquakes or floods. One may need to purchase separate policies for these types of events. It is important to understand what is covered and what is not, to ensure that the right coverage for one’s needs is acquired.
Building insurance covers the structure of the building itself, while property insurance covers the contents of the building. Building under construction insurance is a type of building insurance that is specifically for buildings that are still being built. It covers things like damage to the building and materials, as well as theft or vandalism.
Property insurance, on the other hand, covers things like furniture, appliances, and other belongings in the building. So, the main difference is that building insurance covers the structure itself, while property insurance covers the contents.
All three types of insurance are important, but they cover different things, and NAICOM, the regulator has been campaigning ceaselessly for adherence to laid down codes.
READ ALSO: Our salaries are regular every 25th of the month — Anambra NULGE







