Wellness is an integral part of good health and without wellness, no individual can realise potentials, work productively or contribute meaningfully to the society. Indeed, without wellness, one cannot be said to enjoy good health.
Achieving wellness is however not always easy as it involves mental health which is prone to external triggers; economic situation, emotional upheavals, professional stress, family issues and so many other conditions.

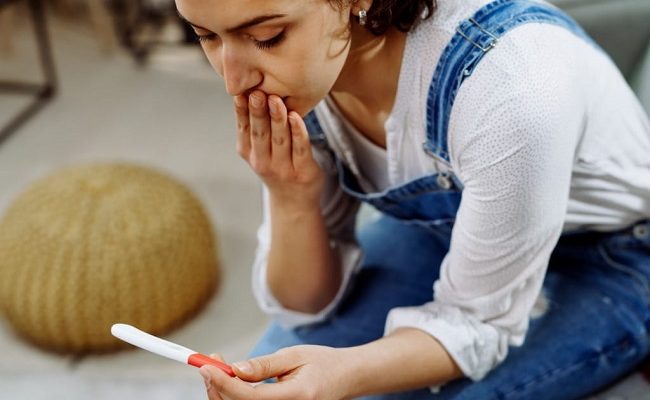
One of the factors that affect mental health is unintended pregnancy which comes in two forms: unwanted pregnancy, that is, a pregnancy that comes when no children are desired and mistimed pregnancy which is pregnancy that occurs earlier than desired.
The truth however is that whether unwanted or mistimed, unintended pregnancies are common; health statistics indicate that in many developing countries, proportion of recent births that are unintended exceeds 40 percent while in Nigeria, an estimated one in five pregnancies is unplanned.
Causes of unintended pregnancies include contraceptive failure, misinformation about reproduction, sexual coercion, abuse or rape and non-usage of available contraceptives.
Unintended pregnancy can occur among all populations of women especially the unmarried, those at either end of reproductive age span (puberty and menopause), uneducated, those with low socioeconomic status, women that abuse psychoactive substances and those that practice s3x trade.
Unintended pregnancy has one major implication; elevated risks of adverse social, economic, physical and mental health outcomes for the mother and child. The effects are far reaching and span the pregnancy period to post partum and through lifetime.
Women that have intended pregnancies usually suffer shame, rejection and stigma during pregnancy. They go through strain on social support risk of safe or unsafe abortion as well as risky antenatal care and delivery.
After delivery, they have issues of poor maternal behaviour especially in terms of breastfeeding, bonding and parenting in addition to health issues like stillbirth and low birth weight. The woman also suffers psychological distress, depression, anxiety, somatisation disorder, post traumatic stress disorder and other mental disorders.
For the child, there is increased risk of infant morbidity and mortality, domestic violence, abuse, poor academic performance, insecure attachments and poor nutritional state.
The child of such unintended pregnancies also suffers mental outcomes like depression, anxiety, attention problems, intellectual disability and other neurodevelopment disorders.
Solution is to prevent unintended pregnancies by addressing gender inequality and cultural taboos surrounding youth and sexuality as well as improving access to sexual and reproductive health services and giving age-appropriate sexuality education.
Unintended pregnancies have far reaching consequences on women involved so there is need for implementation of programs that emphasise pregnancy planning and accessible medical services among other remedies.







