BY SADE OGUNTOLA
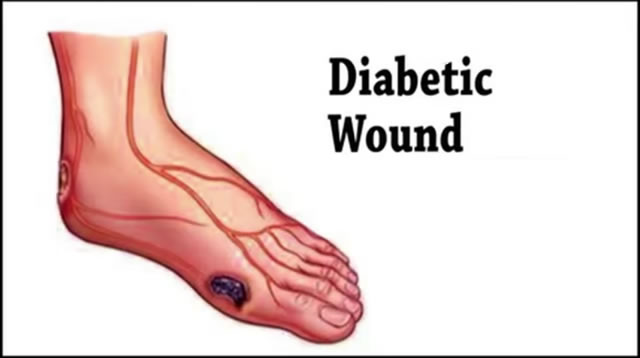
Diabetic wounds are one of the most important issues in diabetic patients. Minor wounds, cuts, and burns are an unfortunate but unavoidable part of life. However, for people with diabetes, wounds can take longer to heal.
This slow healing can increase a person’s risk of developing infections and other complications.
To overcome this challenge, researchers are promoting dressings made from walnut leaf, honey and banana as having the potential to be a new treatment strategy for diabetic wounds. They considerably accelerate diabetic wound healing.
Even when an infection does not develop in a wound, slow healing can adversely affect a person’s overall health and quality of life. Cuts or injuries on the feet or legs can make walking difficult and lead to pain when exercising.
About 34 percent of people with diabetes suffer from diabetic foot ulcers, and about 84 percent of cases lead to foot amputation.

Diabetes impairs how the body produces or responds to insulin, a hormone that allows the cells to take and use glucose from the bloodstream for energy.
This disruption to insulin makes it more difficult for the body to manage blood glucose levels.
In the meantime, herbal medicines have been of interest to the public for a long time, and in recent decades, they have attracted the special attention of researchers. The use of medicinal plants against chemical drugs, in addition to fewer side effects, is economical and safer and more accessible.
One of these plants, which are highly recommended in Iranian traditional medicine, is walnut (Juglans regia L.) The most important parts of this plant are its leaves. Studies have shown that the consumption of walnut leaf extract causes a significant decrease in blood sugar in diabetic patients.
Also, animal studies have shown positive and significant effects of walnut leaf extract in the prevention and treatment of diabetic complications such as damages to the nerves, kidney and eyes. It was said to also attenuate the diabetic complications in the male reproductive organs.
In the present study, the effects of topical administration of walnut leaf extract ointment in two concentrations of two and five percent in diabetic wound healing were investigated.
In general, the researchers found that the extract used in both concentrations had clear and significant effects on all wound healing parameters compared to the other groups. However, these changes were more considerable in the five percent extract group.
The researchers, in the BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, stated “Considering the beneficial effects of Juglans regia L. leaf extract in other complications of diabetes that have been reported previously and our findings in present study, it is suggested to conduct human studies to confirm its effectiveness.”
In the meanwhile, one of the main challenges of wound healing is infection with multi-drug resistant microorganisms like Staphylococcus aureus.
The spectrum of antibiotics used to treat them is declining; thus, there is a need for alternatives.
Researchers said honey can be used as a safer, faster and effective healing agent for diabetic wounds in comparison with other synthetic medications. Honey contains substances said to treat multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, a challenge of wound healing. It was in the journal, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.
Honey was the mainstay of wound healing before the arrival of antibiotics. Numerous scientific reports have demonstrated the success of honey treatments against diabetic wounds.
In a study looking at the role of honey in wound dressing of diabetic ulcers, honey significantly reduced the rate of amputation and improved wound healing.
It included 172 patients with complicated and non-healing diabetic foot ulcers who had their wounds dressed with thick layers of honey. Only three patients (1.75%) underwent big toe amputations.
In comparison, two patients (1.1%) had below-knee amputations leading scientists to conclude that honey can be used as an effective healing agent for diabetic wounds.
Another in the Journal of the Royal Medical Services presented showed that dressings with honey and a standard saline preparation significantly sped up the healing of diabetic foot ulcers and reduced the need for amputations by 50 percent.
In Taiwan, super green (SG) is a newly discovered natural product obtained from banana (Musa paradisiaca) that researchers said can enhance wound repair. In diabetic rats, its topical application ensured heals in surgical wounds.
Excision skin wounds were created on the backs of the rats made to develop diabetes under laboratory conditions. The relevant groups were topically treated with the concentrations of SG or vehicle dressing throughout the study duration. The wound area ratio of the SG-treated group was greatly reduced compared to that of the vehicle-treated group. It was in the 2022 edition of the journal Archives of Medical Science.
READ ALSO FROM NIGERIAN TRIBUNE